219 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
219 lines
8.2 KiB
Markdown
Liquid prompt -- A useful adaptive prompt for Bash & Zsh
|
|
========================================================
|
|
|
|
Liquid prompt is a smart prompt for the "Bourne-Again" Unix shell (bash) and for
|
|
Zsh.
|
|
|
|
The basic idea of the liquid prompt is to nicely display useful informations on
|
|
the shell prompt, only when they are needed. It adds carefuly chosen colors to
|
|
draw your attention on what differs from the normal context. Thus, you will
|
|
notice what changes, when it changes, because you do not become accommodated to
|
|
informations that are always displayed in the same way.
|
|
|
|
You can use it with either bash and zsh.
|
|
|
|
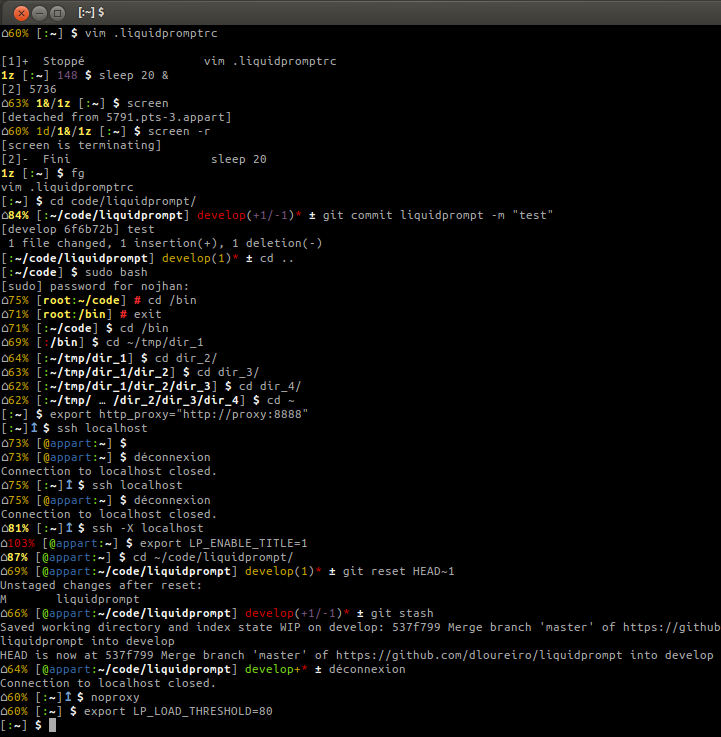
|
|
|
|
## FEATURES
|
|
|
|
If there is nothing special in the current context, the liquid prompt is close
|
|
to a default prompt:
|
|
|
|
`[user:~] $ `
|
|
|
|
If you have ran one command in background that is still running and that you are
|
|
in a git repository on a server, at branch "myb":
|
|
|
|
`1r [user@server:~/liquidprompt] myb ± `
|
|
|
|
A liquid prompt displaying everything may look like this:
|
|
|
|
`⌁24% ⌂42% 3d/2&/1z [user@server:~/ … /code/liquidprompt]↥ master(+10/-5,3) 125 ± `
|
|
|
|
It displays:
|
|
|
|
* a green ⌁ if the battery is charging and above a given threshold,
|
|
a yellow ⌁ if the battery is charging and under threshold,
|
|
a red ⌁ if the battery is discharging but above threshold;
|
|
* the average of the batteries remaining power, if it is under the given
|
|
threshold, with a colormap, going more and more red with decreasing power;
|
|
* the average of the processors load, if it is over a given limit, with a
|
|
colormap that became more and more noticeable with increasing load;
|
|
* the number of detached sessions (`screen`), if there is any;
|
|
* the number of attached sleeping jobs (when you interrupt a command with Ctrl-Z
|
|
and bring it back with `fg`), if there is any;
|
|
* the number of attached running jobs (commands started with a `&`), if there is
|
|
any;
|
|
* the current user, in bold yellow if it is root, in light white if it is not
|
|
the same as the login user;
|
|
* the current host, if you are connected via an SSH or telnet connection, with
|
|
different colors for each case;
|
|
* a green colon if the user has write permissions on the current directory,
|
|
a red one if he has not;
|
|
* the current directory in bold, shortened if it takes too much space, while
|
|
preserving the first two directories;
|
|
* an up arrow if an HTTP proxy is in use;
|
|
* the name of the current branch if you are in a version control repository
|
|
(git, mercurial or subversion), in green if everything is up to date, in red if
|
|
there is changes, in yellow if there is pending commits to push;
|
|
* the number of added/deleted lines, if changes have been made and the number
|
|
of pending commits, if any;
|
|
* the error code of the last command, if it has failed in some way;
|
|
* a smart mark: ± for git directories, ☿ for mercurial, ‡ for svn, $ for simple
|
|
user, a red # for root.
|
|
|
|
You can temporarily deactivate the liquid prompt and come back to your previous
|
|
one by typing `prompt_off`. Use `prompt_on` to bring it back. You can deactivate
|
|
any prompt and use a single mark sign (`$ ` for user and `# ` for root) with the
|
|
`prompt_OFF` command.
|
|
|
|
|
|
## INSTALL
|
|
|
|
Include the file in your bash configuration, for example in your `.bashrc`:
|
|
|
|
`source liquidprompt`
|
|
|
|
Copy the `liquidpromptrc-dist` file in your home directory as
|
|
`~/.config/liquidpromptrc` or `~/.liquidpromptrc` and edit it according to your
|
|
preferences. If you skip this step, the default behaviour will be used.
|
|
|
|
|
|
## DEPENDENCIES
|
|
|
|
Apart from obvious ones, some features depends on specific commands. If you do
|
|
not install them, the corresponding feature will not be available, but you will
|
|
see no error.
|
|
|
|
* battery status need `acpi`,
|
|
* detached sessions is looking for `screen`.
|
|
* VCS support features needs… `git`, `hg` or `svn`, but you knew it.
|
|
|
|
For other features, the script uses commands that should be available on a large
|
|
variety of unixes: `tput`, `grep`, `awk`, `sed`, `ps`, `who`.
|
|
|
|
|
|
## FEATURES CONFIGURATION
|
|
|
|
You can configure some variables in the `~/.liquidpromptrc` file:
|
|
|
|
* `LP_BATTERY_THRESHOLD`, the maximal value under which the battery level is
|
|
displayed
|
|
* `LP_LOAD_THRESHOLD`, the minimal value after which the load average is
|
|
displayed
|
|
* `LP_PATH_LENGTH`, the maximum percentage of the screen width used to display
|
|
the path
|
|
* `LP_PATH_KEEP`, how many directories to keep at the beginning of a shortened
|
|
path
|
|
* `LP_HOSTNAME_ALWAYS`, choose between always displaying the hostname or showing
|
|
it only when connected with a remote shell
|
|
|
|
|
|
## PUT THE PROMPT IN A DIFFERENT ORDER
|
|
|
|
You can sort what you want to see by sourcing your favorite template file
|
|
(`*.ps1`), after having sourced the liquid prompt.
|
|
|
|
Those scripts basically export the `LP_PS1` variable, by appending features and
|
|
theme colors.
|
|
|
|
Available features:
|
|
* `LP_BATT` battery
|
|
* `LP_LOAD` load
|
|
* `LP_JOBS` screen sessions/running jobs/suspended jobs
|
|
* `LP_USER` user
|
|
* `LP_HOST` hostname
|
|
* `LP_PERM` a colon ":"
|
|
* `LP_PWD` current working directory
|
|
* `LP_PROXY` HTTP proxy
|
|
* `LP_GIT` git
|
|
* `LP_HG` mercurial
|
|
* `LP_SVN` subversion
|
|
* `LP_ERR` last error code
|
|
* `LP_MARK` prompt mark
|
|
|
|
Some indicators are not colored by default (mainly those that are _static_), to
|
|
put colors on theme you should not forget to add themed colors variable around
|
|
them:
|
|
|
|
LP_PS1="${LP_ERR}" # no color
|
|
LP_PS1="${LP_COLOR_ERR}${LP_ERR}${NO_COL}" # colored
|
|
|
|
For example, if you just want to have a liquidprompt displaying the user and the
|
|
host, with a normal full path in blue and only the git support:
|
|
|
|
export LP_PS1=`echo -ne "[\${LP_USER}\${LP_HOST}:\${BLUE}\$(pwd)\${NO_COL}] \${LP_GIT} \\\$ "`
|
|
|
|
Note that you need to properly escape dollars in a string that wil be
|
|
interpreted by bash at each prompt.
|
|
|
|
To erase your new formatting, just bring the `LP_PS1` to a null string:
|
|
|
|
export LP_PS1=""
|
|
|
|
|
|
## COLOR THEMES
|
|
|
|
You can change the colors of some part of the liquid prompt by sourcing your
|
|
favorite theme file (`*.theme`), before or after having sourced the liquid prompt.
|
|
|
|
Available colors are:
|
|
BOLD, BLACK, BOLD_GRAY, WHITE, BOLD_WHITE,
|
|
GREEN, BOLD_GREEN, YELLOW, BOLD_YELLOW, BLUE, BOLD_BLUE, PINK, CYAN, BOLD_CYAN
|
|
RED, BOLD_RED, WARN_RED, CRIT_RED, DANGER_RED,
|
|
NO_COL.
|
|
Set to a null string "" if you do not want color.
|
|
|
|
* Current working directory
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_PATH` as normal user
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_PATH_ROOT` as root
|
|
* Color of the proxy mark
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_PROXY`
|
|
* Jobs count
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_JOB_D` Detached (aka screen sessions)
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_JOB_R` Running (xterm &)
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_JOB_Z` Sleeping (Ctrl-Z)
|
|
* Last error code
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_ERR`
|
|
* Prompt mark
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_MARK` as user
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_MARK_ROOT` as root
|
|
* Current user
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_USER_LOGGED` user who logged in
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_USER_ALT` user but not the one who logged in
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_USER_ROOT` root
|
|
* Hostname
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_HOST` local host
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_SSH` connected via SSH
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_TELNET` connected via telnet
|
|
* Separation mark (aka permiison in the working dir)
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_WRITE` have write permission
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_NOWRITE` do not have write permission
|
|
* VCS
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_UP` repository is up to date / a push have been made
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_COMMITS` some commits have not been pushed
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_CHANGES` there is some changes to commit
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_DIFF` number of lines impacted by current changes
|
|
* Battery
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_CHARGING_ABOVE` charging and above threshold
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_CHARGING_UNDER` charging but under threshold
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_DISCHARGING_ABOVE` discharging but above threshold
|
|
* `LP_COLOR_DISCHARGING_UNDER` discharging and under threshold
|
|
|
|
|
|
## KNOWN LIMITATIONS AND BUGS
|
|
|
|
Liquid prompt is distributed under the GNU Affero General Public License
|
|
version 3.
|
|
|
|
* Cannot easily change the colors of features having different state colors
|
|
(like the colormap of the load or the colors of the branch name).
|
|
* detached sessions only looks for `screen`, a `tmux` support would be nice…
|
|
* Does not display the number of commits to be pushed in Mercurial repositories.
|
|
* Browsing into very large subversion repositories may dramatically slow down
|
|
the display of the liquid prompt.
|
|
* Subversion repository cannot display commits to be pushed, this is a
|
|
limitation of the Subversion versionning model.
|
|
* The proxy detection only uses the `$http_proxy` environment variable.
|
|
|